A directory structure in an operating system (OS) is like a map for organizing files and folders. It helps users and the system itself keep everything in order.
This structure is essential for easy navigation, file management, and system efficiency. In this article, we will explore the basics of directory structures, their importance, and how they work in different operating systems.
Directory Structure
A directory structure is a hierarchical way of organizing files and folders in an operating system. It starts from the root directory and branches out into subdirectories and files. This structure allows users to navigate through their files and folders easily.

Importance of Directory Structure
Organization
A well-organized directory structure makes it easier to find and manage files. It prevents clutter and helps keep related files together.
Efficiency
It improves system performance by making file access more efficient. The OS can quickly locate files if they are well-organized.
User Experience
A clear directory structure enhances the user experience by making file navigation intuitive and straightforward.
Types of Directory Structures
Single-Level Directory
In a single-level directory structure, all files are stored in a single directory. This is simple but can become messy and hard to manage as the number of files grows.
Two-Level Directory
This structure has a separate directory for each user. Users have their own files organized in their directory, making it easier to manage files for multiple users.
Tree-Structured Directory
This is the most common type of directory structure. It starts with a root directory and branches out into multiple subdirectories. Each subdirectory can contain files and other subdirectories.
Acyclic-Graph Directory
This structure allows sharing of files and directories among users. It prevents cycles, ensuring that there is no loop in the directory paths.
General Graph Directory
This structure is similar to the acyclic-graph directory but allows cycles. It is more flexible but can be more complex to manage.
Directory Structures Work in Different OS
Windows
In Windows, the directory structure starts with the root directory, usually represented by a drive letter like C:. From there, it branches into folders and subfolders. Common directories include Program Files, Users, and Windows.
Linux/Unix
In Linux and Unix, the directory structure starts with the root directory, represented by /. It branches into directories like /home, /bin, /usr, and /var. Each directory serves a specific purpose, such as storing user files or system binaries.
macOS
macOS also uses a directory structure similar to Unix. The root directory is /, and it branches into directories like /Applications, /Users, and /System. macOS directories are designed to keep system files and user files separate.

Common Directories and Their Purpose
/ (Root Directory)
The top level of the directory structure. All other directories branch from here.
/home
Contains user files and directories. Each user has a separate directory within /home.
/bin
Stores essential binary files needed for the system to function.
/usr
Contains user-related programs and files. It is used for system-wide software.
/var
Stores variable files, such as logs and databases.
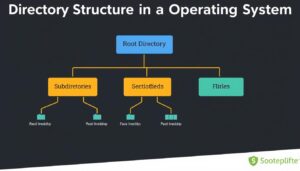
FAQs
What is a directory structure?
A directory structure is a hierarchical way of organizing files and folders in an operating system.
Why is directory structure important?
It is important for organization, efficiency, and enhancing the user experience by making file navigation easy.
What are common types of directory structures?
Common types include single-level, two-level, tree-structured, acyclic-graph, and general graph directories.
How does the directory structure work in Windows?
In Windows, it starts with a root directory (like C:) and branches into folders like Program Files, Users, and Windows.
What are some common directories in Linux/Unix?
Common directories include /home, /bin, /usr, and /var, each serving specific purposes like storing user files or system binaries.
Conclusion
Understanding the directory structure in an operating system is crucial for efficient file management and navigation. Whether you are using Windows, Linux, or macOS, knowing how directories are organized and what each directory is used for can help you keep your system organized and running smoothly.
By following the hierarchical structure, you can ensure that your files are easy to find and manage, enhancing your overall user experience.









