Types of Data Structures
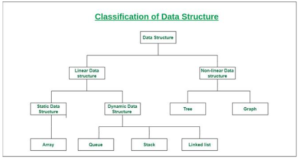
Linear DataStructures
Linear datastructures arrange data in a straight line. Each piece of data has a specific order, like beads on a string. Examples include:
- Arrays: A simple list of items.
- Stacks: Like a stack of plates; you can only add or remove the top item.
- Queues: Like a line of people; the first person in line is the first to be served.
- Linked Lists: A series of connected items, where each item points to the next one.

Static vs. Dynamic DataStructures
- Static DataStructures: These have a fixed size. For example, an array has a set number of slots that can’t change. It’s easy to access any item quickly.
- Dynamic DataStructures: These can change size while the program is running. Examples include linked lists, where new items can be added or removed as needed.
Non-Linear DataStructures
Non-linear data do not arrange data in a straight line. Instead, they organize data in more complex ways. Examples include:
- Trees: Like a family tree, where each item (node) can have many branches.
- Graphs: Like a network of roads connecting different cities.

Common Data Structure and Their Uses
Arrays
Arrays are like a row of lockers where each locker holds one item. You can easily access any item by knowing its position.
Stacks
Stacks work like a stack of books: you can only add (push) or remove (pop) the top book. They are used in undo features in software.
Queues
Queues work like a line at a ticket counter: the first person in line is the first to be served. They are used in scheduling tasks.
Linked Lists
Linked lists are like a chain where each link points to the next. They are flexible and can grow or shrink as needed.

Conclusion
Data structures are vital tools in computer programming. They help us organize data efficiently, make our programs run faster, and keep our code clean and easy to understand. By learning about different data structures and how to use them, we can become better programmers and solve problems more effectively.
FAQ
What is a data structure?
A data structure is a special way to organize and store data in a computer so it can be used efficiently.
Why are data structures important?
They help store and find data quickly, make programs run faster, keep code organized, and are essential for using libraries and frameworks.
What is the difference between linear and non-linear data structures?
Linear data structures arrange data in a straight line, while non-linear datastructures organize data in more complex ways, like trees and graphs.
What is an example of a static datastructure?
An array is an example of a static data structure because it has a fixed size.
How does a stack work?
A stack works like a stack of plates; you can only add or remove the top item, following the Last In, First Out (LIFO) principle.